专用 AI 模型用于执行特定任务或解决特定问题。然而,如果您曾尝试对特定领域的模型进行微调或蒸馏,可能会遇到一些障碍,例如:
- 高质量领域数据不足,特别是针对专有或受监管的应用场景
- 合成数据与模型蒸馏的授权规则尚不明确
- 当大模型无法完成特定任务时,计算成本高昂
- 迭代周期较长,难以实现生产级别的投资回报
这些挑战通常会阻碍前景良好的 AI 项目在实验阶段结束后进一步推进。
本文将向您介绍如何通过生产就绪、许可安全的合成数据蒸馏工作流,消除全部四种障碍。
快速链接
- OpenRouter 上的 Nemotron 3 Nano
- NeMo Data Designer 开源库
- NeMo Data Designer:基于问答示例的产品信息数据集生成工具
- 利用 NeMo Data Designer 构建可蒸馏模型与合成数据处理流程
用于合成数据与知识蒸馏工作流的开源工具
此演示中使用的开源工具包括 OpenRouter,可简化模型访问,和 可蒸的端点,可消除蒸馏资格相关的不确定性。与此同时,NVIDIA NeMo Data Designer 可让您将数据生成流程定义为代码,从而使数据集具备可再现性、可扩展性、可检测性,并能随着需求变化而轻松演进。
所有开发者都能利用这些工具对模型进行专门化,而不仅限于拥有海量数据集或需经历长期法律审查的团队。最终可打造出具备生产就绪能力的专用模型,同时避免合规风险与额外成本。
您将在本教程中构建的内容
本教程将为您介绍一个完整且可重复的工作流程,用于构建兼容的合成数据与知识蒸馏工作流,即使在真实数据稀缺或敏感的情况下亦可适用。
具体而言,您将学习如何:
- 使用 NeMo Data Designer,基于小规模目录和结构化提示生成特定领域的真实产品数据与问答对
- 通过模式定义、采样器及模板提示词,控制数据的多样性与结构
- 利用基于大语言模型的评判标准,自动评估合成数据的答案完整性与准确性,并进行评分与筛选,确保数据质量
- 生成可用于下游知识蒸馏的干净、可安全授权使用的数据集,或通过 OpenRouter 可蒸端点支持微调工作流
虽然此演示采用了产品问答示例,但该模式同样适用于企业搜索、支持机器人、内部工具及其他领域的工作负载。
您将从一个小型种子目录中生成合成数据及问答对。输出为一个结构化数据集,包含产品名称、描述、价格以及相应的问答对。如需查看完整的 NeMo Data Designer:产品信息数据集生成器与问答示例,请访问 NVIDIA/GenerativeAIExamples GitHub 仓库。
为确保数据质量,您将应用 LLM 作为评判 方法,自动对生成的输出进行评分与筛选。在生产环境中,可采用独立的评估模型,但为简化流程,本演练使用同一模型完成生成与评估任务。
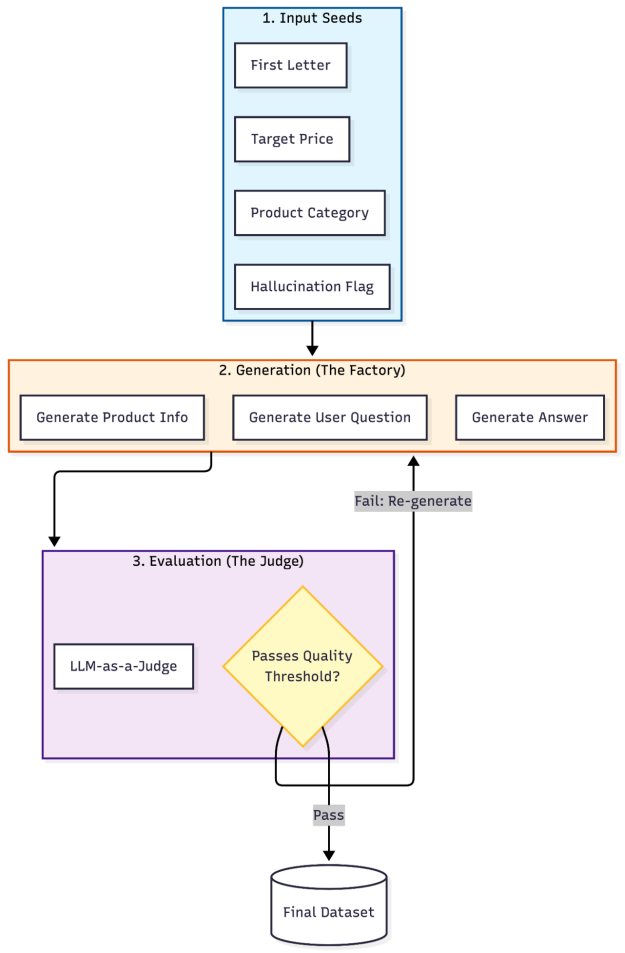
构建合成产品问答数据集
本节介绍构建合成产品问答数据集所涉及的步骤。
初始设置
首先,安装 NVIDIA Data Designer 库:
pip install data-designer==0.4.0
然后导入所需的库:
import data_designer.config as dd
from data_designer.interface import DataDesigner
接下来,创建模型配置文件并初始化 Data Designer 客户端:
# We set trainable text to true here
model_provider = dd.ModelProvider(
name = "deepinfra",
endpoint = "https://openrouter.ai/api/v1/",
provider_type = "openai",
api_key = Open_Router_Api_Key,
extra_body={
"provider": {
"enforce_distillable_text": True,
# optionally, prefer DeepInfra endpoints
"only": ["deepinfra"]
}
}
)
data_designer_client = DataDesigner(model_providers=[model_provider])
在此步骤中,NVIDIA Nemotron 3 Nano 模型通过 OpenRouter 提供服务,并路由至 DeepInfra。启用可蒸实施,以确保所有生成的数据在用于下游训练和蒸馏时均符合许可与安全要求。
接下来,设定生成模型的配置及推理参数:
model_alias="nemotron-3-nano-30b-a3b"
inference_parameters = dd.ChatCompletionInferenceParams(
temperature=0.5,
top_p=0.9,
max_tokens=10000,
max_parallel_requests=10, # Number of concurrent workers
extra_body={
"reasoning": {"enabled": False}
},
)
model_configs = [
dd.ModelConfig(
alias=model_alias,
model="nvidia/nemotron-3-nano-30b-a3b",
provider="deepinfra",
inference_parameters=inference_parameters
)
]
本演示使用 Nemotron 3 Nano 生成合成数据。Nemotron 3 Nano 是 NVIDIA 最新推出的混合式 Mamba MOE 推理模型,专为处理复杂数据结构和实现高效扩展而优化。
该工作流分为三层构建合成问答数据:输入种子、生成与评估。
设计目标数据集架构
在编写任何工作流代码之前,必须明确最终数据集的形态。这将决定哪些部分需要通过大语言模型生成,哪些部分需要采样,以及各部分应如何组合。
此处的目标是生成具备以下特征的结构化、可进行蒸馏的产品问答数据集:
- 每行代表一个产品示例
- 字段包含基础产品属性及生成的自然语言内容
- 该数据集可用于下游训练或蒸馏前的质量筛选
总体来说,每条记录都包含:
- 种子属性(类别、价格区间、命名限制)
- 结构化产品元数据(名称、功能、描述、价格)
- 面向用户的语言(问答形式)
- 质量评分(准确度与完整性)
这种以模式优先的方法可确保数据集具备可重现性、可检查性,并与下游训练需求保持一致。
将数据集模式映射到生成策略
定义目标数据集模式后,下一步是将每一列映射到合适的生成策略。某些字段需要受控的随机性,某些需要结构化的 LLM 输出,而另一些则纯粹用于评估质量。NVIDIA Data Designer 提供了一种声明式的方法,将这些选择以代码形式清晰表达:
config_builder = dd.DataDesignerConfigBuilder(model_configs=model_configs)
数据集中的每一列均属于以下三个类别之一:
- 通过采样生成种子列与控制列,以保障多样性
- 内容列由大语言模型依据结构化提示生成
- 评估列用于对输出质量进行评分与筛选
添加采样器列以控制多样性
这些采样列定义了数据集的可控维度,确保覆盖各类类别、价格范围和命名模式,而无需单独依赖 LLM 的随机性:
import string
from pydantic import BaseModel
from pydantic import Field
# Define product category options
config_builder.add_column(
dd.SamplerColumnConfig(
name="category",
sampler_type=dd.SamplerType.CATEGORY,
params=dd.CategorySamplerParams(
values=[
"Electronics",
"Clothing",
"Home Appliances",
"Groceries",
"Toiletries",
"Sports Equipment",
"Toys",
"Books",
"Pet Supplies",
"Tools & Home Improvement",
"Beauty",
"Health & Wellness",
"Outdoor Gear",
"Automotive",
"Jewelry",
"Watches",
"Office Supplies",
"Gifts",
"Arts & Crafts",
"Baby & Kids",
"Music",
"Video Games",
"Movies",
"Software",
"Tech Devices",
]
),
)
)
# Define price range to seed realistic product types
config_builder.add_column(
dd.SamplerColumnConfig(
name="price_tens_of_dollars",
sampler_type=dd.SamplerType.UNIFORM,
params=dd.UniformSamplerParams(low=1, high=200),
)
)
config_builder.add_column(
dd.ExpressionColumnConfig(
name="product_price",
expr="{{ (price_tens_of_dollars * 10) - 0.01 | round(2) }}",
dtype="float",
)
)
# Generate first letter for product name to ensure diversity
config_builder.add_column(
dd.SamplerColumnConfig(
name="first_letter",
sampler_type=dd.SamplerType.CATEGORY,
params=dd.CategorySamplerParams(values=list(string.ascii_uppercase)),
)
)
# Determine if this example will include hallucination
config_builder.add_column(
dd.SamplerColumnConfig(
name="is_hallucination",
sampler_type=dd.SamplerType.BERNOULLI,
params=dd.BernoulliSamplerParams(p=0.5),
)
)
添加 LLM 生成列
对于需要自然语言或结构化语义内容的列,应采用支持生成的大型语言模型,并指定明确的输出模式。这能确保各条记录之间的一致性,使数据集更适用于后续的训练与评估。
在构建数据集时,必须认识到,LLM 生成的列并非孤立存在,而是有意依托早期的采样器列和种子列,将受控的多样性引入生成过程。
在提示 LLM 时,Jinja 模板可用于引用数据集中其他列的值,例如采样类别、价格或命名限制。这些输入直接影响 LLM 的输出,使系统能够引入多样性,而不仅依赖提示的随机性。此外,还可通过点符号访问嵌套的 JSON 字段,从而让结构化输出自然地贯穿整个工作流。
例如,结构化 ProductInfo 输出以产品类别、product_price 以及名称约束条件等采样值为条件,确保上游引入的多样性能够在所有 LLM 生成的字段中持续传播。
# Define product information structure
class ProductInfo(BaseModel):
product_name: str = Field(
..., description="A realistic product name for the market."
)
key_features: list[str] = Field(
..., min_length=1, max_length=3, description="Key product features."
)
description: str = Field(
...,
description="A short, engaging description of what the product does, highlighting a unique but believable feature.",
)
price_usd: float = Field(..., description="The stated price in USD.")
# Generate product information
config_builder.add_column(
dd.LLMStructuredColumnConfig(
name="product_info",
model_alias=model_alias,
prompt=(
"Generate a realistic product description for a product in the {{ category }} "
"category that costs {{ product_price }}.\n"
"The name of the product MUST start with the letter {{ first_letter }}.\n"
),
output_format=ProductInfo,
)
)
# Generate user questions about the product
config_builder.add_column(
dd.LLMTextColumnConfig(
name="question",
model_alias=model_alias,
prompt=("Ask a question about the following product:\n\n {{ product_info }}"),
)
)
# Generate answers to the questions
config_builder.add_column(
dd.LLMTextColumnConfig(
name="answer",
model_alias=model_alias,
prompt=(
"{%- if is_hallucination == 0 -%}\n"
"<product_info>\n"
"{{ product_info }}\n"
"</product_info>\n"
"{%- endif -%}\n"
"User Question: {{ question }}\n"
"Directly and succinctly answer the user's question.\n"
"{%- if is_hallucination == 1 -%}\n"
"Make up whatever information you need to in order to answer the user's request.\n"
"{%- endif -%}"
),
)
)
使用 LLM 评委进行质量评估
LLM 即用于评判以确保数据质量。清晰的评估等级有助于在下游应用前对生成答案的完整性和准确性进行评分。
# Define evaluation rubrics for answer quality
CompletenessRubric = dd.Score(
name="Completeness",
description="Evaluation of AI assistant's thoroughness in addressing all aspects of the user's query.",
options={
"Complete": "The response thoroughly covers all key points requested in the question, providing sufficient detail to satisfy the user's information needs.",
"PartiallyComplete": "The response addresses the core question but omits certain important details or fails to elaborate on relevant aspects that were requested.",
"Incomplete": "The response significantly lacks necessary information, missing major components of what was asked and leaving the query largely unanswered.",
},
)
AccuracyRubric = dd.Score(
name="Accuracy",
description="Evaluation of how factually correct the AI assistant's response is relative to the product information.",
options={
"Accurate": "The information provided aligns perfectly with the product specifications without introducing any misleading or incorrect details.",
"PartiallyAccurate": "While some information is correctly stated, the response contains minor factual errors or potentially misleading statements about the product.",
"Inaccurate": "The response presents significantly wrong information about the product, with claims that contradict the actual product details.",
},
)
# Evaluate answer quality
config_builder.add_column(
dd.LLMJudgeColumnConfig(
name="llm_answer_metrics",
model_alias=model_alias,
prompt=(
"<product_info>\n"
"{{ product_info }}\n"
"</product_info>\n"
"User Question: {{question }}\n"
"AI Assistant Answer: {{ answer }}\n"
"Judge the AI assistant's response to the user's question about the product described in <product_info>."
),
scores=[CompletenessRubric, AccuracyRubric],
)
)
# Extract metric scores for easier analysis
config_builder.add_column(
dd.ExpressionColumnConfig(
name="completeness_result",
expr="{{ llm_answer_metrics.Completeness.score }}",
)
)
config_builder.add_column(
dd.ExpressionColumnConfig(
name="accuracy_result",
expr="{{ llm_answer_metrics.Accuracy.score }}",
)
)
预览数据集
要在缩放前检查数据集,可先生成一个小的预览,并将结果加载到 pandas DataFrame 中:
preview = data_designer_client.preview(config_builder)
# Display one record
preview.display_sample_record()
表 1 列出了合成产品问答记录的示例,展示了输入的种子属性(类别、价格、幻觉标志)、由大语言模型生成的详细信息与问答内容,以及大语言模型对准确性和完整性所评定的质量分数。
| 字段名称 | 价值/ 生成内容 |
| 类别 (种子) | 服装 |
| 起始字母 (种子) | D |
| Hallucination 标志 | 1 (启用创意模式) |
| 产品名称 | Driftwood 豪华开士米混合毛衣 |
| 产品价格 | 545.57 美元 |
| 用户问题 | 是什么让 Driftwood 豪华开士米混合毛衣特别适合都市优雅与户外冒险 … …? |
| AI 答案 | 这件毛衣融合了可持续来源的开士米与美利奴羊毛 |
| — | — |
| 准确性评分 | ⚠️ 部分准确 |
| 准确性理由 | 答案正确描述了毛衣的豪华理念,但编造了材料成分(美利奴羊毛,回收尼龙)并夸大了性能声明(徒步旅行,滑雪)在提供的产品信息中不存在。 |
| 完整性评分 | ⚠️ 部分完整 |
| 完整性理由 | 响应地址都市优雅和可持续来源,但引入了未提及的材料并省略了产品源中提到的特定“隐藏内衬口袋”。 |
扩展数据生成
在模式和质量检查效果良好的基础上,通过增加记录数量来生成规模更大的数据集:
job_results = data_designer_client.create(config_builder, num_records=100)
dataset = job_results.load_dataset()
保存结果
随后,将生成的数据集保存为 pandas DataFrame,用于下游的训练、评估或蒸馏工作流程:
from pathlib import Path
Folder_Name = "data-designer-tutorial-output"
File_Name = "dataset_OR.csv"
TUTORIAL_OUTPUT_PATH = Path(Folder_Name)
TUTORIAL_OUTPUT_PATH.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
dataset.to_csv(TUTORIAL_OUTPUT_PATH / File_Name, index=False)
工作流程优势
通过将 OpenRouter 与 NVIDIA 开源工具相结合,开发者能够更高效、更安全地实现模型的专业化:
- 内置合规性:通过可蒸馏端点生成具备许可证安全性的合成数据
- 高质量领域数据,赋能特定任务模型:利用 NeMo Data Designer 快速构建特定领域的结构化数据集,缩短企业级定制化模型的开发周期
借助此工作流,您能够绕过通用大语言模型,构建可理解领域规则、解析高层目标并支持复杂工作流程的专用模型。
开始使用专为蒸馏优化的合成数据集
本教程重点介绍如何设计和生成适合蒸馏的合成数据集。若要开始使用,并将生成的数据应用于模型训练、蒸馏及部署的下一阶段,请参考以下资源:
- Nemotron 3 Nano: 开放且高效的推理模型,经批准可用于蒸馏工作流程,适合作为教师模型
- NVIDIA NeMo Data Designer: 用于定义、版本控制和扩展合成数据工作流的开源工具
- OpenRouter 蒸馏指南: 通过统一 API 进行蒸馏并提供任务优化模型的实用指南
- NeMo Data Designer:具备问答功能的产品信息数据集生成器示例: 一个可运行的端到端示例,可根据您的模式和领域灵活调整
- 使用 NeMo Data Designer 构建可蒸馏模型与合成数据工作流: 概述 OpenRouter 提供的可授权且安全的合成数据生成方案,以及 NVIDIA NeMo Data Designer 对蒸馏工作的支持
访问 Nemotron 开发者页面,获取启动最开放、最智能的每计算推理模型所需的所有资源。





