NVIDIA TensorRT LLM 使开发者能够为大语言模型 (LLM) 构建高性能推理引擎,但传统上部署新架构往往需要大量手动工作。为应对这一挑战,今天我们宣布在 TensorRT LLM 中推出 AutoDeploy 作为测试版功能。
AutoDeploy 可将现成的 PyTorch 模型编译为经过推理优化的计算图。这种方式无需将特定于推理的优化直接嵌入模型代码中,从而显著缩短 LLM 的部署时间。AutoDeploy 支持从手动重新实现并优化每个模型的传统做法,转向由编译器驱动的自动化工作流,实现模型创作与推理优化的分离。
本文将介绍 AutoDeploy 的架构与功能,并展示其在发布时对最新 NVIDIA Nemotron 模型的支持。
什么是 AutoDeploy?
从 Transformer 模型到混合视觉语言模型 (VLM),再到状态空间模型 (SSM),每种新的 LLM 架构都带来了独特的推理挑战。将参考实现转化为高性能推理引擎,通常需要引入 KV 缓存管理、在 GPU 间进行权重分片、操作融合,以及针对特定硬件优化执行图。
AutoDeploy 将此工作流程转变为由编译器驱动的方法。借助 AutoDeploy,模型开发者无需手动重新实现推理逻辑,系统可自动从现成的 PyTorch 模型中提取计算图,并通过一系列自动化转换,生成针对推理优化的 TensorRT LLM 图。这使得您只需在 PyTorch 中定义一次模型,即可将推理相关的复杂问题(例如缓存管理、模型分片、内核选择以及运行时集成)交由编译器与运行时系统自动处理。
这种方法特别适合长尾模型,包括新的研究架构、内部变体以及快速迭代的开源模型,在这些场景中,手动重新实现往往不切实际或难以持续。AutoDeploy 支持在启动时以具有竞争力的基准性能进行部署,同时在模型逐步成熟的过程中,保留清晰的增量优化路径。
AutoDeploy 提供:
- 无缝模型转换: 自动将 Hugging Face 模型转换为 TensorRT LLM 图形,无需手动重写
- 单一事实来源: 保持原始 PyTorch 模型作为标准定义
- 推理优化: 集成分片、量化、KV 缓存插入、注意力融合及 CUDA 图形优化等技术
- 启动时部署: 支持即时部署,并随时间推移持续提升性能
- 一站式设置: 作为 TensorRT LLM 的一部分发布,配套提供示例与文档
AutoDeploy 可用于:
- 新架构或实验架构: 支持快速部署研究模型、混合设计或新型 token 混合(注意力)机制
- 长尾模型支持: 无需定制推理实现,即可服务内部模型、微调模型或较少见的模型
- 快速性能启动: 迅速达到竞技级基准性能,并支持后续持续优化
- 统一的训练到推理工作流: 保持 PyTorch 作为模型定义语言,同时依托 TensorRT LLM 实现运行时集成
AutoDeploy 目前支持 100 多个文本转文本 LLM,并为 VLM 和 SSM 模型,以及 Llama 模型系列和 NVIDIA Nemotron 3 Nano 等经过性能优化的模型提供早期支持。
AutoDeploy 技术背景
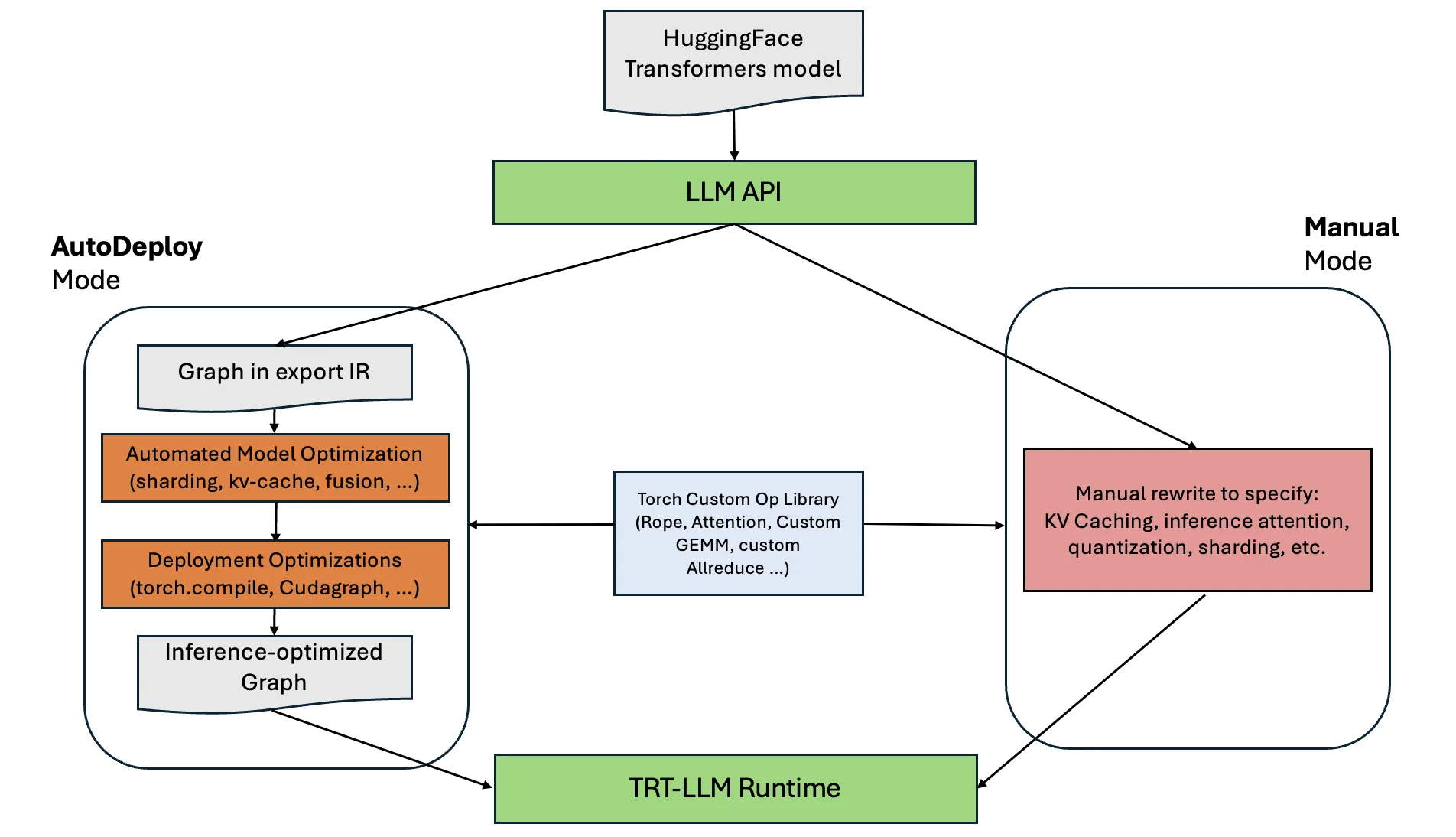
AutoDeploy 位于原始 Hugging Face 模型与 TensorRT LLM 运行时之间。LLM API 接受模型名称或检查点目录,并返回一个高级 LLM 对象。在后台,该对象可使用 AutoDeploy(自动)或手动指定的后端。
如图 1 所示,AutoDeploy 路径可自动提取图形,应用优化,并生成经过推理优化的图形。而手动路径则要求工程师在通过相同运行时运行模型前,对模型进行重写(包括添加 KV 缓存逻辑、注意力内核、分片、内核融合等)。
图形捕获和模式匹配
AutoDeploy 使用 torch.export API 以标准化的 Torch 图形形式捕获模型,该图形由核心 ATen 操作以及自定义操作(由用户或 AutoDeploy 提供)构成。随后,导出的图形会经历一系列自动转换,用于模式匹配,并对常见构建块的图形表示进行规范化。
在此初始步骤中,AutoDeploy 可确保常见的构建块(如混合专家 (MoE)、注意力、RoPE 或状态空间层)通过图形中表示为自定义运算和单节点的参考实现来呈现。
图 2 提供了一个示例,展示了注意力机制如何在所有模型中被表示为 PyTorch 中一个易于理解的自定义算子。
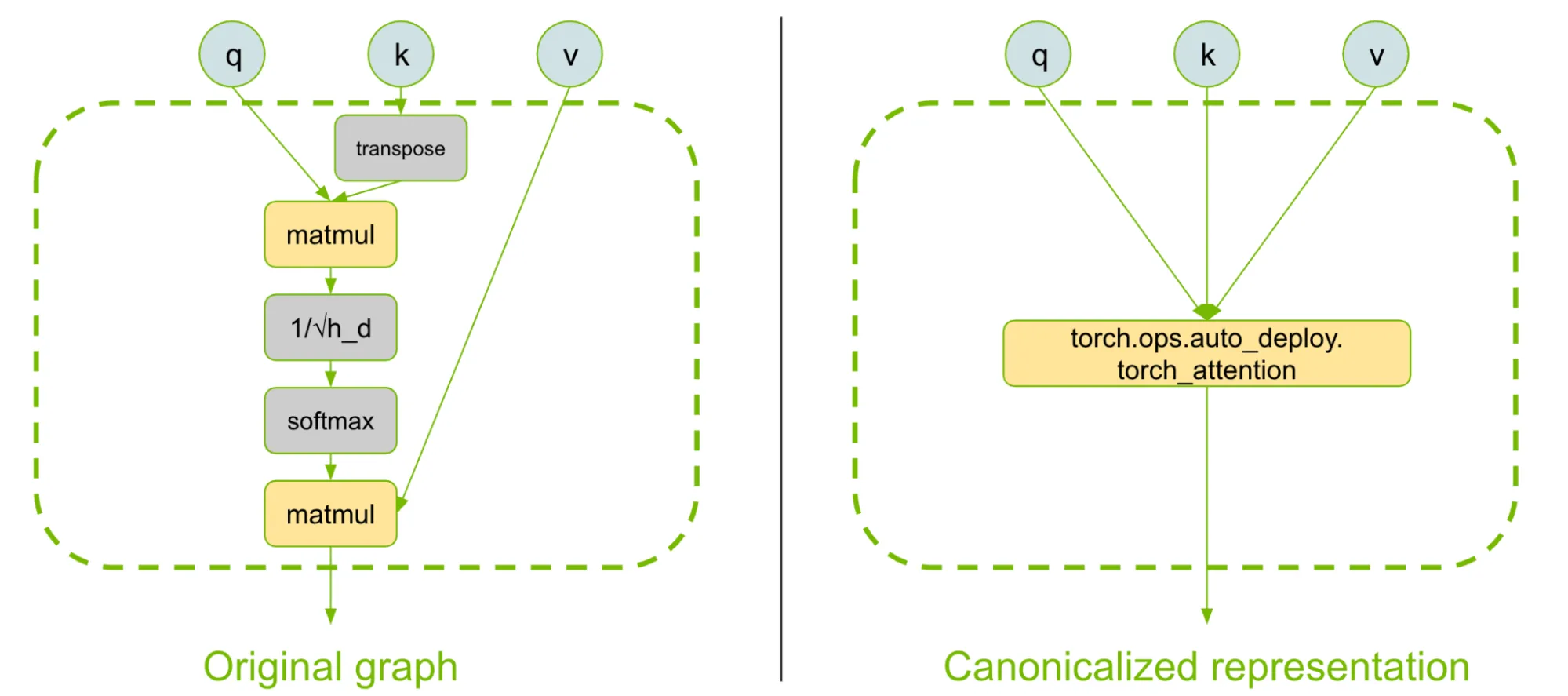
这种方法可确保模型支持的无缝加载过程与性能优化及运行时集成相互分离。
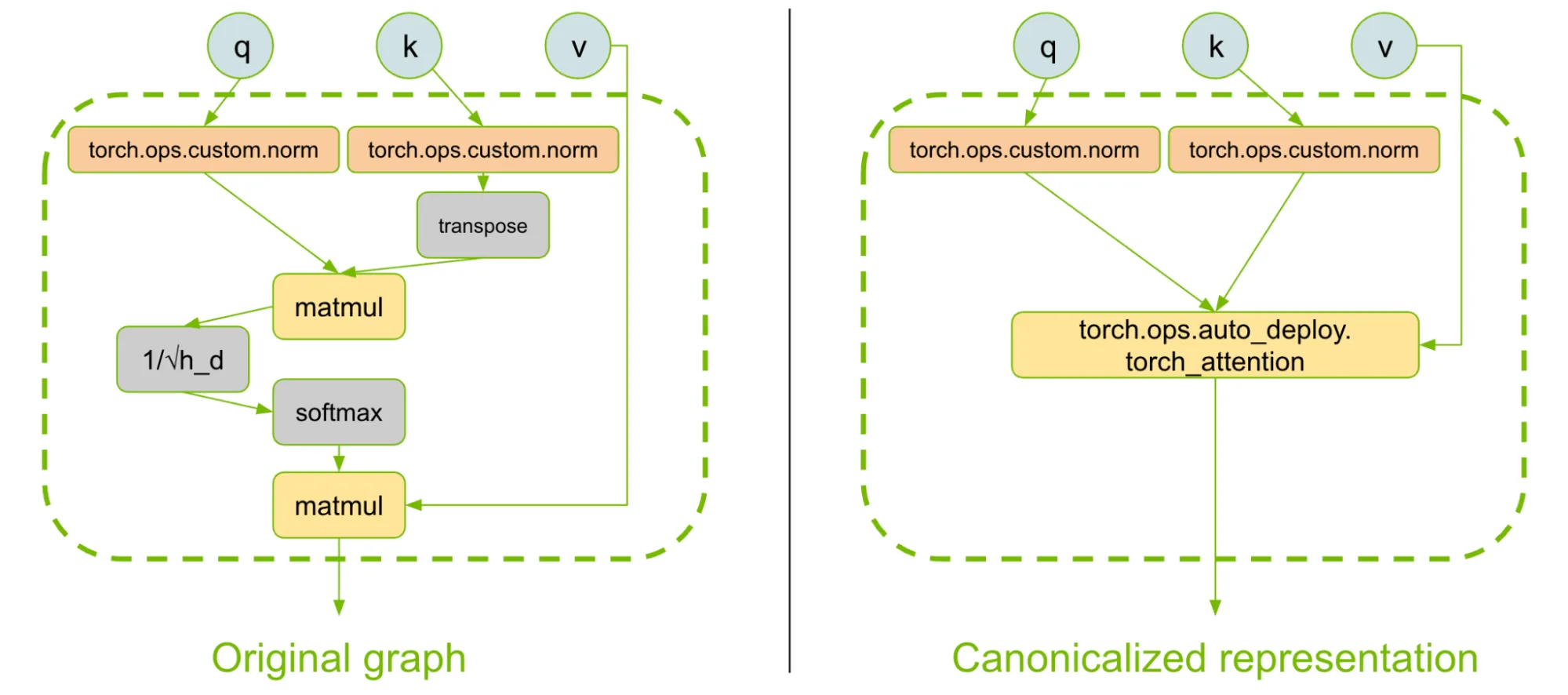
此外,模型载入在通过模式匹配实现全自动载入与(完全)手动重写之间按滑动比例进行,以确保最终的模型图能够完整执行模型。模型作者可将相关运算标注为 PyTorch 自定义算子。AutoDeploy 编译器不会修改这些算子(图 3)。
分片、融合和性能优化
在下一阶段,AutoDeploy 通过类似编译器的传递过程自动应用性能优化,将算子融合、性能调优方法以及优化后内核的插入整合到图表示中。在此阶段,系统还会依据可用的启发式策略或预先指定的分片提示,重用 Hugging Face 的分片建议,对模型进行划分,以支持多 GPU 推理。<!–
支持灵活的注意力和缓存
在图形捕获和模式匹配过程中,AutoDeploy 将 token 混合(例如注意力)运算符表示为简化的仅预填充操作,并将其表示为 AutoDeploy 规范化参考运算符。图 3 展示了 softmax 注意力的示例。
然后,系统会自动完成性能优化的注意力内核切换,并将 token 混合运算符的缓存机制自动集成到 TensorRT LLM 优化的缓存管理器系统中。目前,AutoDeploy 可支持由 softmax 注意力、状态空间层(Mamba2)、线性注意力(DeltaNet)和因果卷积任意组合构成的模型。
添加对其他具有缓存功能的运算符的支持需遵循严格的接口规范,且易于扩展。
编译工具
AutoDeploy 与常见的现成工具集成,支持进一步编译和模型压缩,例如 torch.compile,同时集成 CUDA 图形以实现固定批量大小的仅解码推理,并支持多流优化等功能。
运行时集成
AutoDeploy 可处理将模型集成到优化的 TensorRT LLM 运行时的各个方面,涵盖重叠调度程序、分块预填充、预测解码以及缓存和状态管理等功能,同时避免让模型作者承担模型与运行时之间复杂交织的依赖关系。
AutoDeploy 性能示例:Nemotron 3 Nano
为了评估 AutoDeploy 功能,该团队采用了混合 MoE 模型 NVIDIA Nemotron 3 Nano。手动调优此类模型以进行推理通常需要数周时间,而 AutoDeploy 能在几天内完成部署,并在此基础上根据手动调优的基准进行增量优化。
在单个 NVIDIA Blackwell DGX B200 GPU 上,AutoDeploy 的性能与 TensorRT LLM 中手动优化的基准相当(图 4)。它可为每位用户提供高达 350 tokens 的吞吐量,并分别为低延迟和高吞吐量应用提供高达 13000 token 的输出。
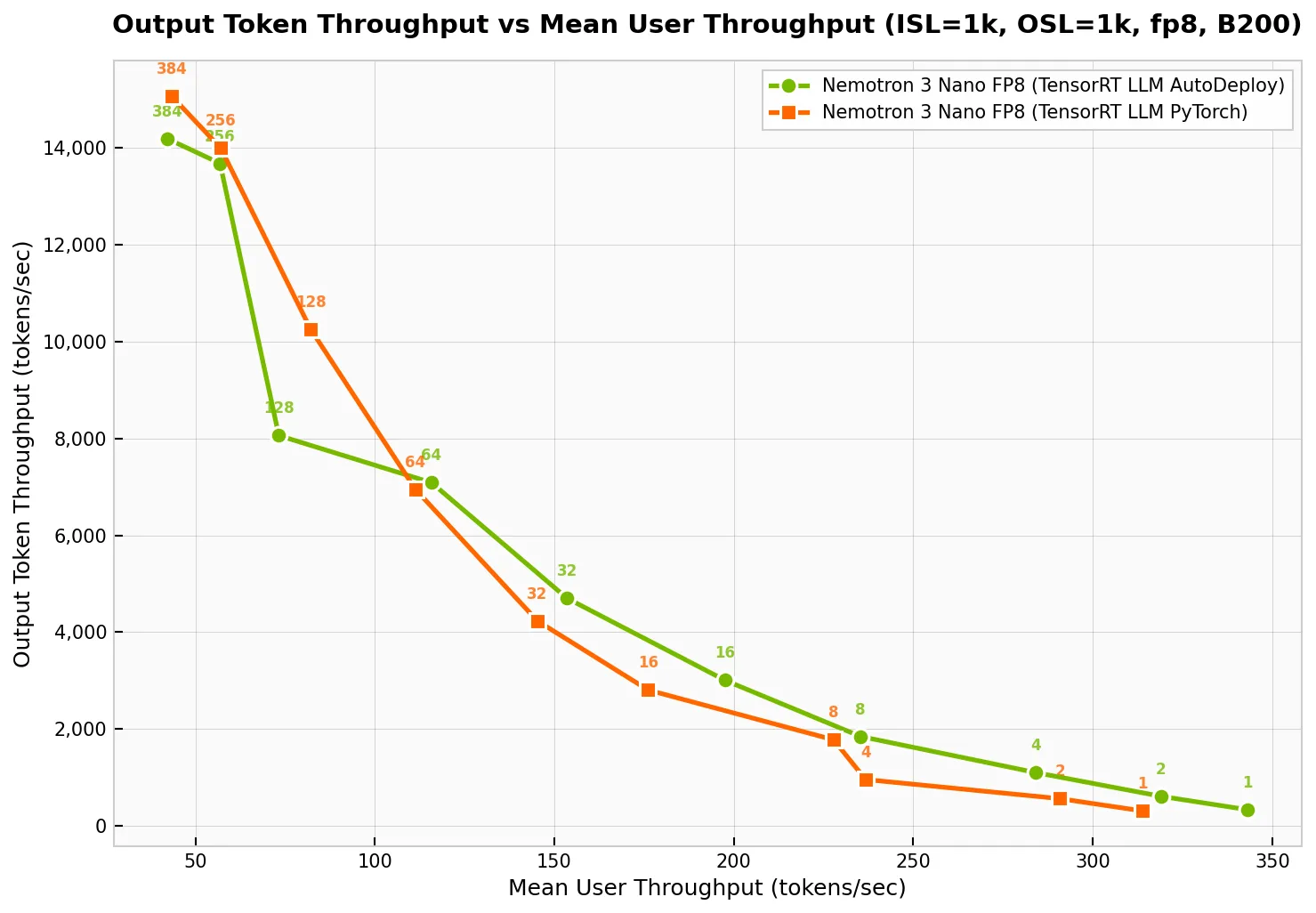
我们使用 TensorRT LLM v1.3.0rc1、trtllm-serve ,和 AIPerf 基准测试工具,对 NVIDIA DGX B200 上的 ISL/OSL 1k/1k、TP = 1 场景进行了数据采集。
要自行复制结果,请依照 NVIDIA Nemotron 3 Nano Checkpoint 中所述的步骤进行操作。
模型载入示例:Nemotron-Flash
Nemotron-Flash 是典型架构类型的示例,采用纯手动推理工作流程难以支持此类架构。这种混合研究模型融合了多种 token 混合器(包括状态空间层、softmax 注意力和线性注意力),需要大量工程工作来进行手动重新实现、优化和维护。
借助 AutoDeploy,Nemotron-Flash 层现有的优化通道可直接复用,无需进行任何模型特定的工程工作。新的层类型(例如 DeltaNet 更新规则)以增量扩展的形式集成,而非完全重写,可在未来模型加载任务中重复使用。<!–
因此,Nemotron-Flash 在几天内便完成了载入和性能优化,现已实现开箱即用。这凸显了 AutoDeploy 的核心优势:一旦优化被表示为可复用的编译器通道,新模型和非常规架构便能立即受益于完整的优化堆栈,在保持高推理性能的同时显著缩短部署周期。
该团队使用 TensorRT LLM AutoDeploy 对 Nemotron Flash 3B Instruct 与 Qwen2.5 3B Instruct 进行基准测试,其中 Qwen2.5 3B Instruct 是一个广泛应用且需要大量手动调优的模型,二者模型规模相近。在图 1 所示的基准测试场景(ISL/OSL = 8k/16k)中,Nemotron-Flash 的性能优于 Qwen2.5,凸显了新型模型架构能够快速部署并实现生产级性能的潜力。
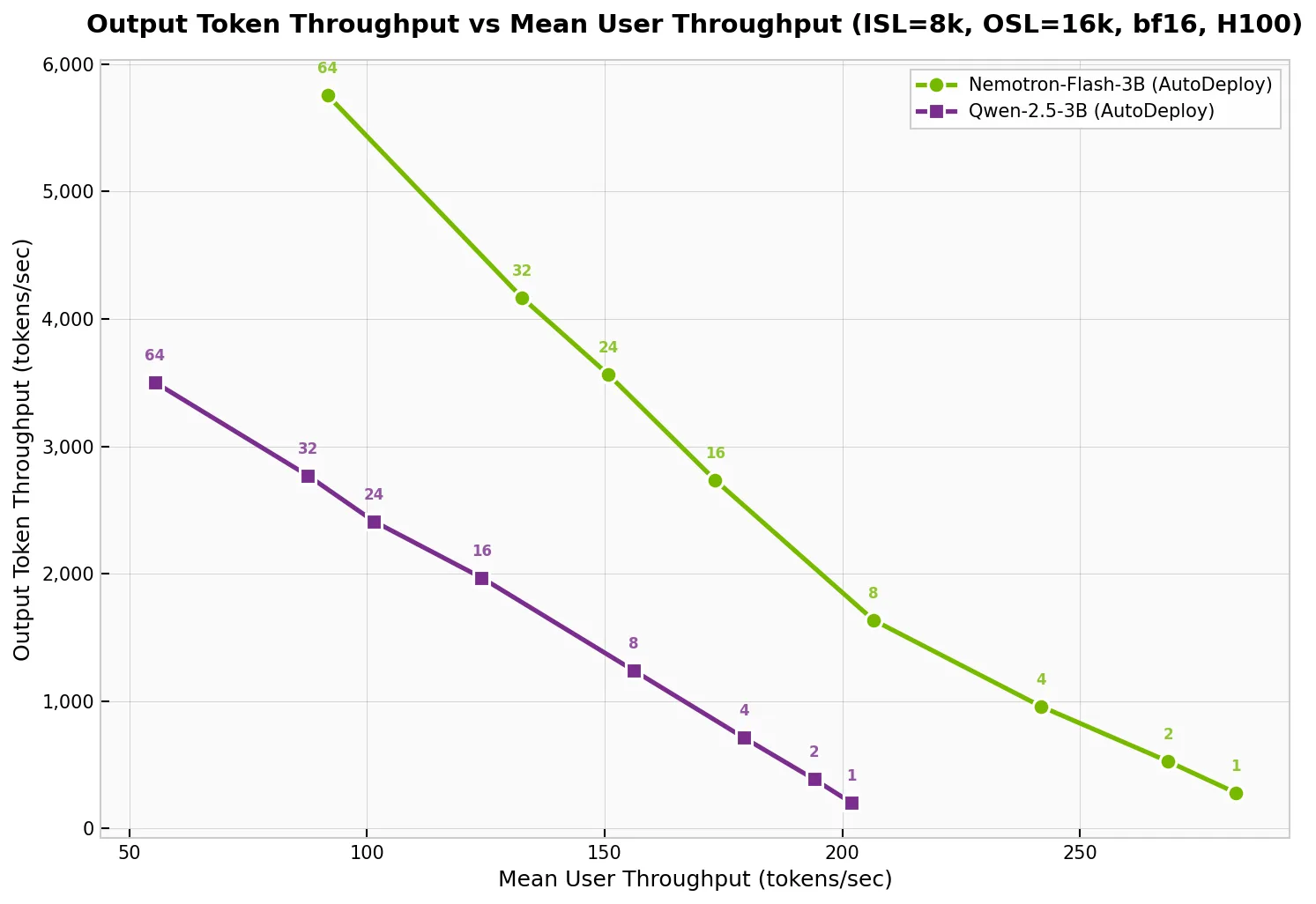
我们使用 TensorRT LLM v1.3.0rc1、trtllm-serve ,和 AIPerf 基准测试工具,在 NVIDIA DGX H100 上对 ISL/OSL 8k/16k、TP = 1 进行了数据采集。
开始使用 TensorRT LLM AutoDeploy
TensorRT LLM AutoDeploy 标志着推理优化正逐渐被视为编译器与运行时的责任,而非模型作者的负担。这一方法有助于加快实验迭代、拓展模型支持范围,并更清晰地分离模型设计与部署工作。
您无需手动调整每个模型,只需描述一次架构,系统便可自动应用图形转换与优化的内核。Nemotron Nano 3 和 Nemotron-Flash 等早期成功案例表明,针对不同模型架构,可在模型发布时实现峰值性能的部署。
TensorRT LLM AutoDeploy 正在快速发展。如果您有兴趣体验此功能或参与其开发,欢迎查阅 AutoDeploy 文档 和 示例脚本。
致谢
我们要感谢为 AutoDeploy 做出贡献的人员,包括 Ajinkya Rasane、Bala Marimuthu、Chenghao Zhang、Chenjie Luo、Eran Geva、Frida Hou、Gal Hubara Agam、govind Ramnarayan、Grzegorz Kwasniewski、Hao Guo、Jingyu Xin、Joyjit Daw、Karthik Vetrivel、Lucas Liebenwein、Neta Zmora、Suguna Varshini Velury、Suyog Gupta、Tal Cherckez、Taylor Lee、Wanli Jiang、Wei-Ming Chen、William Zhang 等。





